SBR (Sequencing-Batch-Reactor)-Process
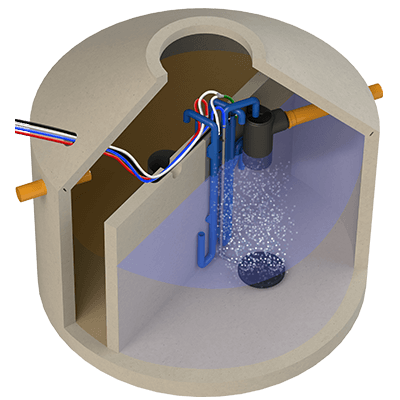
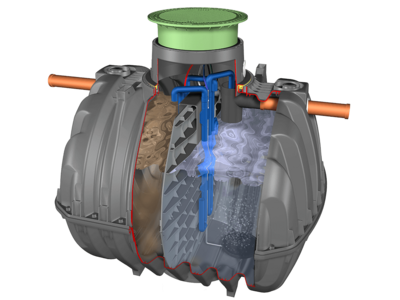
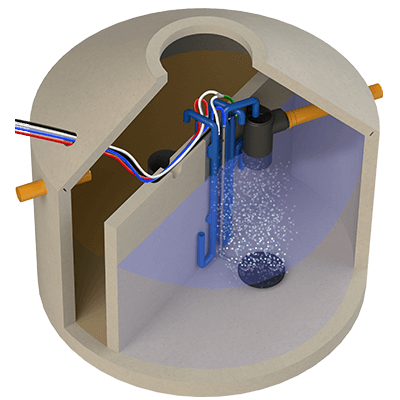
SBR stands for "Sequence Batch Reactor". The process is also known as "Activation process in accumulation operation". The fully biological wastewater treatment is carried out with activated sludge; growth bodies are not required. The activated sludge consists mainly of microorganisms which decompose the pollutants dissolved in the wastewater. The special feature is that the clarification processes in the SBR-reactor do not take place spatially separated, but according to a time sequence ("clarification cycle"). The inflowing wastewater is collected by a buffer, purified in portions and discharged at the end of a treatment cycle.
Advantages of the SBR process
- Insensitive to hydraulic shock loads (are absorbed by the buffer)
- Stable cleaning performance
- Very good clarification result
- Effective operating mode
- Well controllable - possibilities for readjustment
- Also suitable for underload operation
- Largely independent of container geometry
Main differences to other systems
- No pumps in the septic tank that are susceptible to faults and blockages
- No growth bodies necessary
- Clarification processes not spatially separated, but in chronological order
- No secondary sedimentation tank necessary
- No continuous flow, but changing water levels depending on inlet or cycle
- Water levels can be measured and thus the system can be controlled depending on the filling level (according to demand) instead of fixed time control
SBR sewage treatment plants by KLARO
KLARO offers two SBR processes for small wastewater treatment plants and larger plants.
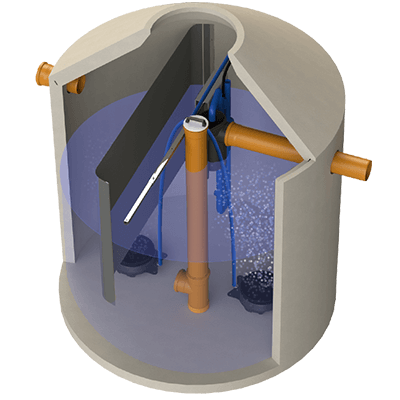
System KLARO
A two-stage SBR process.
Here, the SBR reactor is preceded by a sludge storage tank and buffer.
System KLARO One
A single-stage SBR process with aerobic sludge stabilization.
The septic tank does not necessarily have to contain several chambers.